In today’s fast-evolving world of automation and smart control, relay systems play a crucial role in managing electrical circuits efficiently. Whether for industrial automation, home automation, or advanced IoT applications, understanding the core components of relay control can make a significant difference in system performance and flexibility.
This comprehensive guide explores four essential topics in relay technology: the versatility of a programmable relay, the functionality of an 8 channel relay board, the specialized features of the PoRelay8, and the broader applications of an io controller. Each of these components serves a unique purpose, enabling precise control over electrical devices, seamless automation, and integration into complex systems.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how these technologies work, their key benefits, and how they can be applied in real-world scenarios. Whether you’re an engineer, a hobbyist, or a tech enthusiast, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of relay-based control systems. Let’s dive into the first chapter: the power and flexibility of a programmable relay.
What Is a Programmable Relay and How Does It Work?
A programmable relay is a versatile device designed to control electrical circuits through customizable logic, making it an essential component in automation systems. Unlike traditional relays, which operate based on fixed mechanical or electrical inputs, a programmable relay can be configured using software to execute complex switching tasks. This adaptability allows engineers and technicians to tailor the relay’s behavior to specific applications without modifying hardware.
One of the key advantages of a programmable relay is its ability to replace multiple hardwired relays and timers with a single, compact unit. By using built-in logic functions—such as timing, counting, sequencing, and conditional operations—these relays simplify circuit design and reduce wiring complexity. For example, in industrial machinery, a programmable relay can automate processes like motor control, conveyor belt sequencing, or safety interlocks, all while being reprogrammed on the fly for different tasks.
Another important feature of a programmable relay is its compatibility with various input and output (I/O) signals. Many models support digital inputs (like push buttons or sensors) as well as analog inputs (such as temperature or pressure readings). The relay processes these signals according to its programmed logic before activating the appropriate outputs, which could include motors, solenoids, or even other relays. Some advanced versions also offer communication protocols like Modbus, Ethernet, or wireless connectivity, enabling integration into larger control networks.
A common application of a programmable relay is in building automation, where it can manage lighting, HVAC systems, or security devices based on time schedules or sensor inputs. In home automation, these relays can be used to create smart lighting scenes or energy-saving routines. Because they are reprogrammable, they offer future-proof flexibility, allowing users to update logic as requirements change.
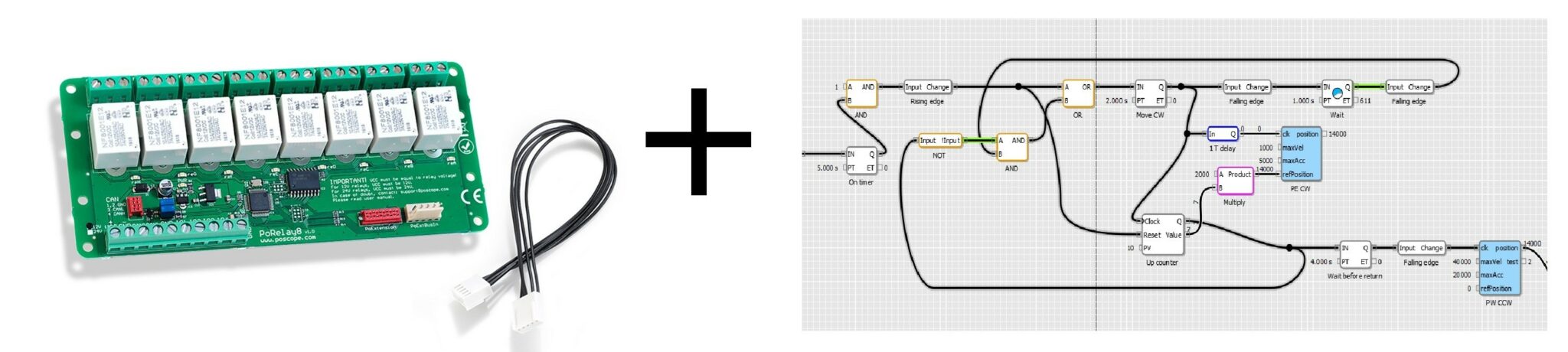
In summary, a programmable relay is a powerful and adaptable solution for automation tasks, offering significant advantages over conventional relays. Its ability to execute custom logic, reduce wiring complexity, and integrate with multiple control systems makes it indispensable in modern electrical and electronic applications. The next chapter will explore another critical component: the 8 channel relay board, which expands control capabilities even further.
What Is an 8 Channel Relay Board and Where Is It Used?
An 8 channel relay board is a compact yet powerful module that allows users to independently control up to eight different electrical circuits using a single interface. These boards are widely used in automation, IoT projects, and industrial control systems where multiple devices need to be switched on or off remotely or programmatically. Unlike a single relay module, an 8 channel relay board provides scalability, enabling more complex control schemes without requiring multiple individual relays.
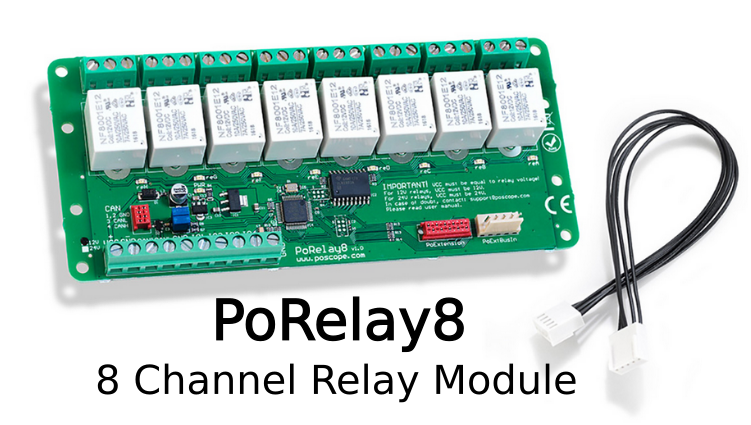
One of the primary advantages of an 8 channel relay board is its ability to handle high-voltage and high-current loads, making it suitable for controlling appliances, motors, lights, and other heavy-duty equipment. Each channel typically consists of an electromechanical or solid-state relay, optocouplers for electrical isolation, and driver circuitry to ensure safe and reliable operation. The board can be interfaced with microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or PLCs, allowing for seamless integration into custom automation projects.
A common use case for an 8 channel relay board is in home automation, where it can manage multiple lighting zones, fans, or security systems from a central hub. In industrial settings, these boards are often deployed in machinery control, conveyor systems, or testing equipment where sequential or conditional switching is required. The ability to control multiple circuits simultaneously also makes them ideal for laboratory setups, agricultural automation (such as irrigation control), and entertainment systems like stage lighting.
Another key feature of many 8 channel relay boards is their support for different control voltages (e.g., 5V, 12V, or 24V), making them compatible with a wide range of control systems. Some models include additional functionalities such as status LEDs, manual override switches, or screw terminals for easy wiring. Advanced versions may also support communication protocols like I2C or SPI, enabling daisy-chaining of multiple boards for expanded control capacity.
In summary, an 8 channel relay board is a versatile and efficient solution for managing multiple electrical loads in both consumer and industrial applications. Its modular design, ease of integration, and robust performance make it a go-to choice for engineers and hobbyists alike. The next chapter will introduce the PoRelay8, a specialized relay module with unique features that further enhance automation possibilities.
Understanding Stepper Motor Drivers and Their Applications
What Makes the PoRelay8 a Unique and Powerful Relay Solution?
The PoRelay8 stands out in the world of relay control systems by combining the flexibility of an 8 channel relay board with the added convenience of Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) capability. This innovative integration allows the PoRelay8 to receive both power and control signals through a single Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for separate power supplies while enabling remote management over a network. This makes it an ideal solution for applications where centralized control, reduced wiring complexity, and reliable connectivity are critical.
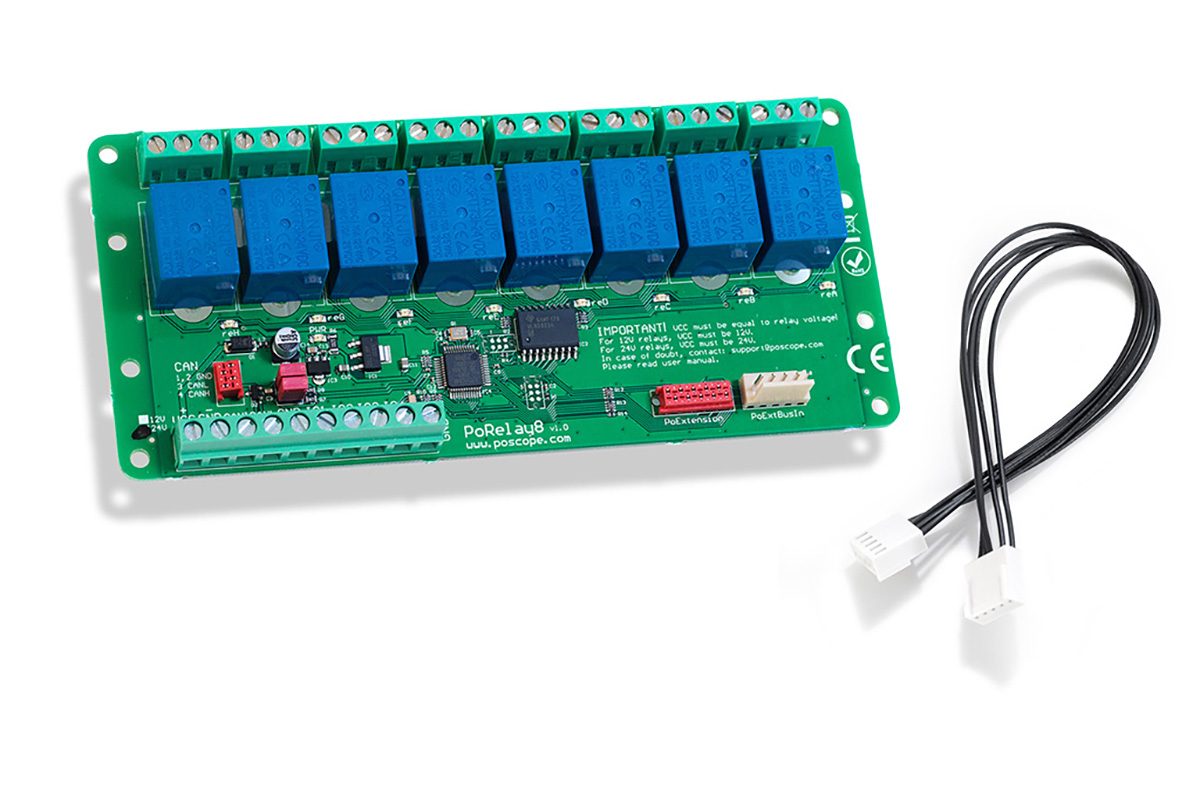
One of the most significant advantages of the PoRelay8 is its seamless integration into networked automation systems. Unlike traditional relay boards that require direct connections to microcontrollers or PLCs, the PoRelay8 can be controlled via standard Ethernet protocols, including TCP/IP and HTTP. This allows users to operate the relay channels from anywhere on the network—whether through a local server, a cloud-based dashboard, or even a mobile app. For industrial IoT (IIoT) applications, this remote accessibility ensures real-time monitoring and control without physical intervention.
The PoRelay8 is designed for both versatility and robustness, often featuring optically isolated relays to protect control circuits from electrical noise and voltage spikes. Each of the eight channels can typically switch high-current loads, making it suitable for applications such as smart building automation, industrial machine control, and distributed power management. Additionally, some models include built-in safeguards like overload protection and fail-safe modes to ensure system reliability.
A practical use case for the PoRelay8 is in smart office environments, where it can manage lighting, HVAC systems, and security devices through a centralized network. In industrial settings, it can coordinate multiple machines or safety shutoffs across a factory floor without requiring extensive wiring. The PoE functionality also makes it an excellent choice for installations in hard-to-reach locations, such as ceiling-mounted lighting controls or outdoor monitoring systems, where running separate power lines would be impractical.
In summary, the PoRelay8 redefines relay control by merging the simplicity of PoE with the power of multi-channel switching. Its ability to streamline installations, reduce wiring costs, and provide remote access makes it a standout choice for modern automation projects. The next chapter will explore the broader role of an io controller in managing relay systems and other peripheral devices.
What Is an IO Controller and How Does It Enhance Relay Automation?
An IO controller (Input/Output controller) serves as the central brain in automation systems, managing communication between sensors, relays, and other connected devices. Unlike standalone relay modules, an IO controller provides advanced programmability, allowing complex logic, real-time monitoring, and seamless integration with broader control systems. When paired with relay boards like the PoRelay8 or an 8 channel relay board, it transforms simple switching operations into sophisticated automation sequences.
One of the key strengths of an IO controller lies in its ability to process multiple input signals and trigger precise output responses. For example, in an industrial setting, it can read data from temperature sensors, pressure switches, or motion detectors, then activate specific relays to control motors, valves, or alarms based on predefined conditions. This decision-making capability makes it far more powerful than basic timer-based or manual relay control. Many modern IO controllers also support programmable logic controller (PLC) functionality, bridging the gap between simple relay automation and full-scale industrial control systems.
Another advantage of using an IO controller is its connectivity. Most models support standard industrial protocols like Modbus, CAN bus, or Ethernet/IP, enabling them to communicate with HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces), SCADA systems, and cloud platforms. This allows operators to monitor and adjust relay operations remotely, collect performance data, and even implement predictive maintenance algorithms. In smart agriculture, for instance, an IO controller could manage irrigation relays based on soil moisture sensors while logging data to optimize water usage over time.
The IO controller also excels in scalability. While a single 8 channel relay board handles eight devices, multiple boards can be linked to an IO controller to expand control capacity into dozens or hundreds of channels. Some controllers even feature modular designs, where additional I/O modules—such as analog inputs or wireless transceivers—can be added as needed. This flexibility makes them suitable for everything from small home automation projects to large-scale manufacturing lines.
In summary, an IO controller elevates relay automation by adding intelligence, connectivity, and scalability. By serving as the command center for sensors and actuators, it enables more efficient, adaptable, and data-driven control systems. The final chapter of this guide will tie these concepts together, exploring how programmable relays, multi-channel boards, PoE-enabled devices, and IO controllers work in harmony to create cutting-edge automation solutions.
The Future of Automation: Integrating Relays and Intelligent Control
From the adaptable programmable relay to the network-ready PoRelay8, relay technology has evolved far beyond simple electrical switches. These components—alongside scalable solutions like the 8 channel relay board and the decision-making power of an io controller—form the backbone of modern automation systems. Together, they enable smarter, more efficient control across industries, from manufacturing and energy management to smart homes and IoT ecosystems.
The true potential of these technologies emerges when they work in unison. A programmable relay handles custom logic for individual processes, while an 8 channel relay board expands control to multiple devices. The PoRelay8 eliminates wiring complexity with PoE connectivity, and an io controller orchestrates everything with centralized intelligence. This integration reduces hardware costs, minimizes downtime, and unlocks advanced functionalities like remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven optimization.
As automation continues advancing, relay systems will remain essential—but their role will shift toward greater connectivity and intelligence. Future innovations may include AI-enhanced io controllers, self-diagnosing relays, and even tighter integration with wireless and cloud-based platforms. One thing is certain: whether you’re an engineer designing a factory line or a hobbyist automating your home, understanding these core components will be key to building efficient, future-ready systems.
By mastering the principles of programmable relays, multi-channel boards, PoE-enabled devices, and intelligent controllers, you’re not just working with technology—you’re shaping the automated world of tomorrow. The journey starts with a single switch, but the possibilities are limitless.
Solving Plasma Cutting Challenges: How PlasmaSensOut and Smart Z-Axis Deliver Flawless Results